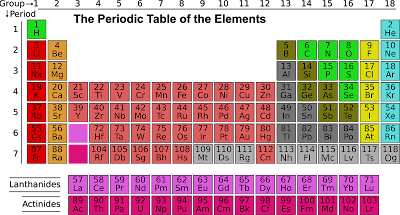
The periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular display of the chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and chemical properties. The elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of an element. Each element is placed in a specific location on the periodic table based on its atomic structure and its chemical properties, which are determined by the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus. The periodic table is a useful tool for understanding the properties of the elements and predicting their behaviors in chemical reactions. It is also a useful reference for finding information about the elements, such as their atomic weights, melting points, and boiling points. The periodic table is divided into 18 vertical columns, called "groups," and 7 horizontal rows, called "periods." The elements in a group have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons, which are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom that are involved in chemical reactions. The elements in a period have similar physical and chemical properties because they have the same number of electron shells.
The elements in the periodic table are also classified as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids. Metals are good conductors of electricity and heat, and they are generally shiny, malleable, and ductile. Nonmetals are poor conductors of electricity and heat, and they are generally brittle and not shiny. Metalloids have properties of both metals and nonmetals.
The periodic table also includes several categories of elements that have special properties. For example, the noble gases are a group of elements that are extremely unreactive, and the halogens are a group of elements that are highly reactive and form compounds with most other elements. The lanthanides and actinides are also special categories of elements that are located at the bottom of the periodic table.
In addition to its basic layout and organization, the periodic table includes a number of additional features that provide information about the elements. For example, the atomic weight of each element is listed on the periodic table, and the elements are also color-coded to indicate their chemical properties. The periodic table also includes a series of boxes that are used to represent the electron configurations of the elements and to predict their chemical properties.


Comments
Post a Comment